Table of Contents
The DevOps Crisis at Scale
When you're a 5-person startup, deployments are simple: one person manually runs tests, updates servers, and hopes nothing breaks. It works.
But as you scale:
- One person becomes a bottleneck—every deployment waits for them
- Manual testing misses bugs; they escape to production
- Deployments take hours and require a designated "deployment master"
- Rollbacks take forever because you're not sure what changed
- Engineers waste 40% of their time on deployment/ops instead of building product
The solution? DevOps—a practice that aligns development and operations, automating the full workflow from code commit to production deployment.
Understanding the DevOps Value Chain
Traditional Model: Developers write code → Testers manually test → Operations deploys → Customers use it (slowly)
DevOps Model: Developers write code → Automated tests verify → Automated deployment to staging → Manual approval → Automated production deployment → Continuous monitoring → Feedback loops → Repeat
The difference? Speed and quality improve simultaneously. More deployments, fewer bugs, less manual work.
The Five Pillars of DevOps Implementation
1. Automated Testing
No DevOps without testing automation. If you're manually testing, you're not DevOps—you're just hoping.
- Unit tests: Test individual functions (easiest, fastest)
- Integration tests: Test components working together
- End-to-end tests: Test complete user workflows
- Security scanning: Automated vulnerability scanning
- Performance testing: Catch performance regressions early
2. Continuous Integration (CI)
Every code commit triggers automated tests. If tests fail, developers know immediately—before it reaches production.
Real-world impact: A team committing code 20x per day can catch and fix bugs the same day they're introduced.
3. Continuous Deployment (CD)
Passing code flows automatically through staging and production with zero manual intervention (or one-click approval).
This sounds risky but is actually safer—frequent, small deployments are lower risk than quarterly "big bang" releases.
4. Infrastructure as Code
Your infrastructure is defined in code, version-controlled, and deployed like application code. This enables:
- Reproducible environments
- Disaster recovery (rebuild from code)
- Collaboration and code review
- Audit trails and compliance
5. Monitoring & Observability
You can't improve what you don't measure. Real-time monitoring of application health, performance, and errors enables fast incident response and continuous optimization.
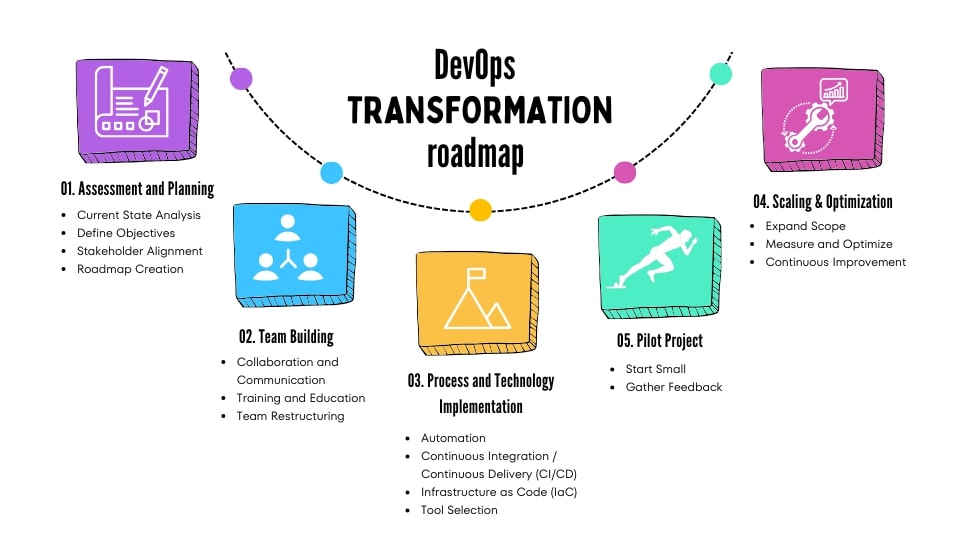
The 12-Week DevOps Transformation Roadmap
Month 1: Foundation (Automated Testing & Version Control)
Week 1-2: Audit current testing. Most startups have <10% test coverage. We'll plan to increase to 60%+.
Week 3-4: Implement automated test suite (unit tests, integration tests). Establish code review process in Git.
Deliverable: Every merge request requires passing tests before it can be merged.
Month 2: CI/CD Pipeline (Automated Builds & Staging Deployment)
Week 5-6: Set up CI/CD platform (GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, or Jenkins).
Week 7-8: Configure pipeline: code commit → automated tests → automated staging deployment.
Deliverable: Every merge to main branch automatically deploys to staging and notifies the team.
Month 3: Production Deployment & Monitoring
Week 9-10: Configure production deployment (with approval gate). Set up monitoring (Datadog, New Relic, Prometheus).
Week 11-12: Document runbooks, set up alerting, practice incident response.
Deliverable: One-click production deployments. Production health visible in dashboards. Incidents trigger immediate notifications.
Quick Wins for Teams Already Using Git
Week 1: Add GitHub Actions
GitHub Actions is free for public repos and extremely affordable for private repos. Configure basic CI: run tests on every PR.
Week 2: Add Security Scanning
Enable Dependabot to automatically scan dependencies for vulnerabilities. Catch supply chain attacks before they reach production.
Week 3: Add Staging Deployment
Extend CI to automatically deploy passing code to a staging environment. Enable the team to test before production.
Tools for Your DevOps Stack
| Purpose | Tools | Why |
| Version Control | GitHub, GitLab | Industry standard |
| CI/CD | GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, Jenkins | GitHub Actions easiest; free tier is generous |
| Testing | Jest, Pytest, RSpec | Language-specific frameworks |
| Deployment | Vercel, Netlify, AWS CodeDeploy | Cloud-native deployment |
| Monitoring | Datadog, New Relic, Prometheus | Real-time system visibility |
Expected Results After 12 Weeks
- Deployment Frequency: From 1-2x monthly → 10-20x weekly (10x improvement)
- Deployment Time: From 4+ hours → 15 minutes
- Bug Escape Rate: From 30-40% → <5% (bugs caught in CI, not production)
- Incident Response: From 2+ hours → 15 minutes (automated rollback available)
- Engineer Time on Ops: From 40% → <10%
Common DevOps Mistakes to Avoid
- Testing too late: Tests must run on every commit, not batch-tested before release
- Not automating deployment: If deployment still requires 4+ manual steps, you're not doing DevOps
- Skipping monitoring: You can't fix what you don't see. Monitoring is as important as deployment
- No rollback plan: If something breaks in production, you need instant rollback, not a 2-hour investigation
- Treating DevOps as tooling: It's not about tools; it's about culture. Tools enable the culture
Ready to transform your DevOps workflow? Sahi Technologies helps startups and SMBs implement CI/CD, automated testing, and deployment automation. We can assess your current workflow and recommend a transformation roadmap. Schedule Free Assessment →